Critical Path vs. Critical Chain: In-Depth Comparison of Scheduling Methods
Audio version:
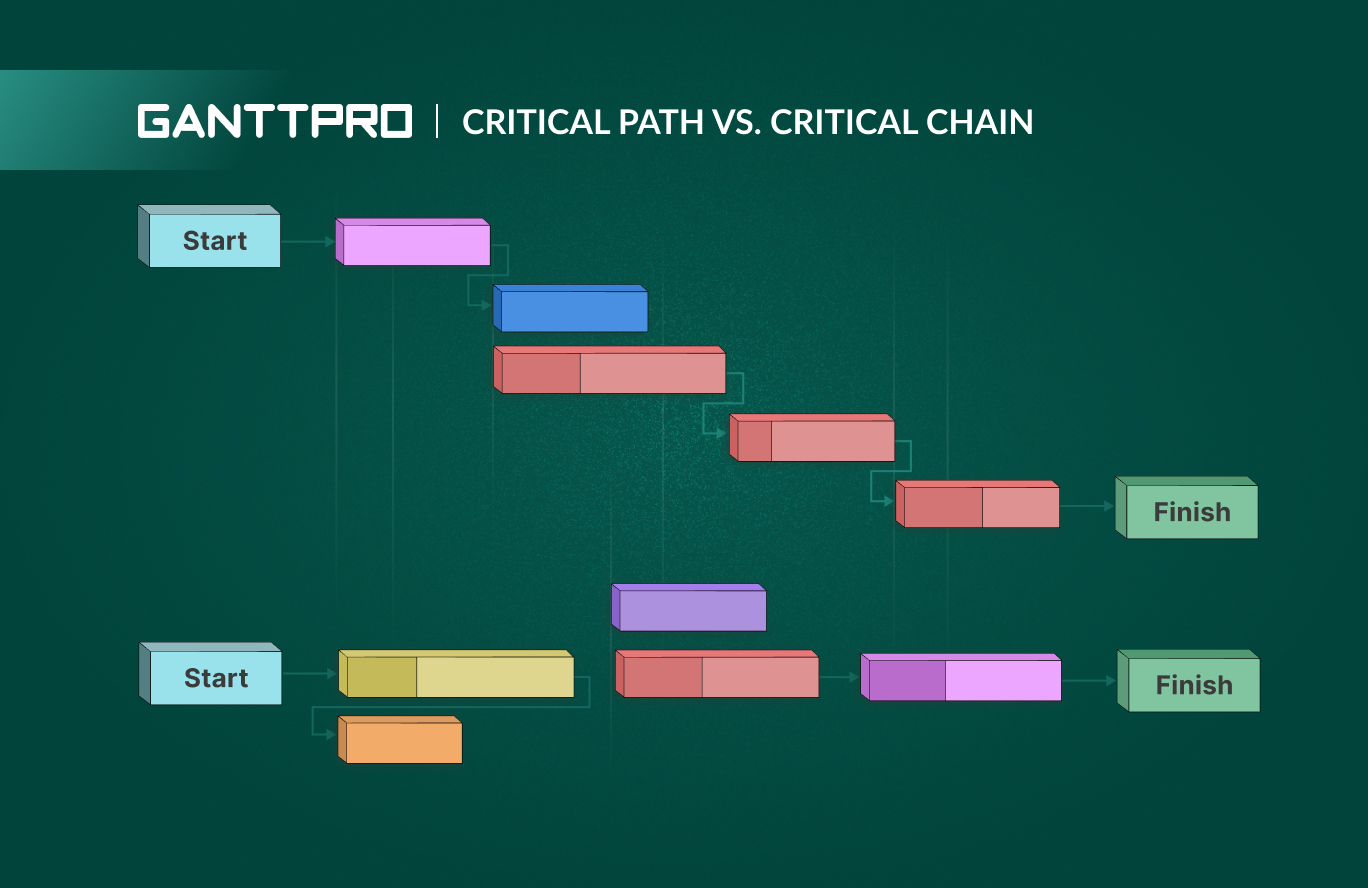
Teams worldwide identify a critical path in their projects to ensure timely project completion and schedule adherence. They use the critical path method (CPM) in various industries. However, a thorough analysis of project management issues resulting from this approach prompted the development of the more sophisticated critical chain method (CCM).
The critical path vs. critical chain comparison has become the subject of discussion among many professionals. At first glance, both concepts are very similar. They determine the critical sequence of dependent tasks and required project resources. However, when delving further into the processes, it becomes clear that the methods differ.
In this article, we explore the core differences between the critical path method vs. critical chain method and share a step-by-step example of finding crucial tasks using a reliable critical path planner.
Contents:
- What the critical path method is.
- The benefits of the critical path method.
- What the critical chain method is.
- The benefits of the critical chain method.
- Critical path vs. critical chain: what’s the difference?
- How to use a critical path in GanttPRO.
Critical path method
The critical path method in project management is an approach used for identifying the sequence of important tasks and activities that need to be finished promptly to guarantee the project’s successful and timely completion.
As well as the famous PERT chart in project management, CPM helps teams easily visualize the overall flow of their tasks. However, a more detailed visual representation of this method can be made with the help of a handy Gantt chart.
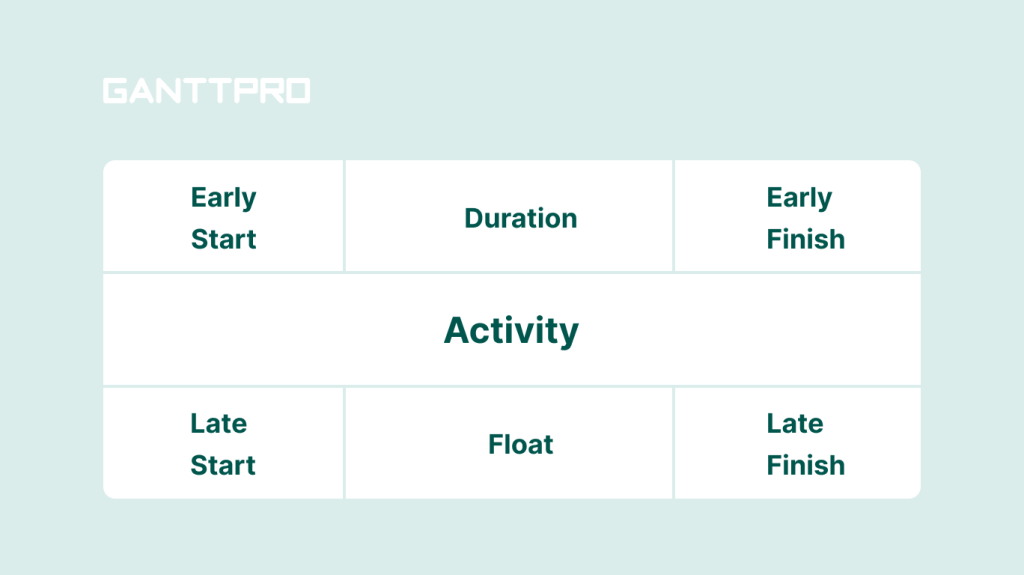
CPM involves the calculation of early start (ES), early finish (EF), late start (LS), and late finish (LF) through forward and backward passes in a project schedule diagram. It helps project managers estimate the buffers (floats) or their lack of individual activities on a scheduled path.
Critical tasks cannot be postponed because it will lead to project delays. However, if the activities on your critical path are completed ahead of schedule, the whole project will be completed quicker.
Where did the idea of the critical path method come from?
CPM originated in the United States in the late 1950s. It was developed by two engineers, James Kelley Jr. and Morgan Walker, who worked at the DuPont company. Their efforts were initially aimed at planning and managing maintenance projects and then evolved into the use of the critical path method in construction.
It has become a widely used method in various industries for scheduling and managing simple and complex projects. You can find bright critical path examples in software development, construction, manufacturing, healthcare, and other spheres.
Dessy Tsolova, the founder of FASHION INSIDERS & CO, an online fashion educational platform, has been studying the effect of using a critical path in apparel projects and the manufacturing industry in general for several years. She notes:
A critical path in manufacturing is nothing new. It’s just another project-managing element that you have to add to everything else. Without a critical path, you are going to have chaos. Without a critical path, you won’t be able to effectively delegate your sampling and production. If you’re working in a team or looking to expand your business, you need a critical path.
Now let’s define the most evident advantages of CPM.
Benefits of the critical path method
The pros and cons of the critical path method are a popular topic for discussion among project managers. However, the strengths prevail.
Below we share the key benefits of the critical path method.

- Clear project schedule. CPM offers a detailed project schedule that highlights all critical tasks and their dependencies. It facilitates project timeline visualization and enhances understanding of all project plan parts.
- Effortless identification of a critical path. The method identifies core activities that influence the project’s overall duration, helping project managers prioritize on-time completion.
- Proper resource allocation. If you wonder how to allocate resources properly, CPM will definitely assist as it demonstrates when and where particular resources are needed. The combination of the method and professional resource management software assists in preventing overallocation or underutilization of all project assets.
- Advanced risk management. CPM enables teams to spot potential project delays and their impact on a timeline, supporting proactive risk management and mitigation.
- Boosted communication. CPM provides a visual representation of a project schedule, making it easier to communicate progress and timelines to clients and stakeholders.
- Seamless performance tracking. By comparing planned schedules with actual progress, CPM empowers project managers to track performance and implement necessary adjustments.
Now it’s time to learn more about the second approach from our review, as well as find out the main differences between critical chain vs. critical path.
Critical chain method
The critical chain method is actually built on the critical path method.
CCM is also used to plan, schedule, and execute projects more efficiently. It’s related to CPM but focuses on resource constraints and project buffers.
The method suggests treating a project similarly to a relay race. It means that it’s better to complete each task quickly before passing it on to the next person, emphasizing the overall goal rather than individual tasks.
To apply CCM, PMs need to estimate the project’s completion time and allocate 50% of that time as the baseline duration in project planning. The remaining time serves as a buffer for handling tasks and additional activities that might be added toward the end of a project.
Where did the idea of the critical chain method come from?
CMM was described by Dr. Eliyahu Goldratt in the early 1990s in his book. The author designed the method as part of his broader work in operations management and project management to improve work scheduling and performance.
After a detailed analysis of project management problems using the critical path method, Goldratt proposed his approach to solving them.
He highlighted the following theses:
- To use time estimates with 50% uncertainty overlap.
- To protect performers from management pressure in case of missed deadlines.
- To concentrate not on determining the deadline for completing each task, but preferably on the date of the end of a project as a whole.
- To enter a margin of time to compensate for uncertainty for a project (project buffer).
- To introduce alerts to resources employed on a critical chain that it will soon be necessary to switch to complete a task for this project (resource buffer).
- To introduce a temporary reserve for coverage uncertainty (feeding buffer) when performing work on a non-critical chain.
Thus, Goldratt began the formation of a new method in project management, which his followers further developed. It quickly gained popularity in manufacturing project management, construction, and other fields.
Here’s how Simon Wallis, a project manager at GSK, a global biopharma company, evaluates the role of the critical chain project management, applied and adapted to their product pipeline:
Our company already has an extremely strong product pipeline. But the timelines in which we were required to deliver new products were becoming a challenge. Using the critical chain approach, we were able to simplify processes at key points, and also make the process of project delivery more transparent and collaborative. We were able to take advantage of real practical opportunities to iron out problems that we were seeing on a day-to-day basis and really improve the whole project delivery process.
There is also a vivid example of CCM implementation and product performance improvement carried out in the sphere of device development.
Philip Marris, the founder of Marris Consulting, describes the workflow and details of this project in the insightful video.
The project managed with the help of a critical chain was aimed at creating a medical machine for diagnosing respiratory infections. In order to speed up the development of this machine, the management decided to implement the critical chain method.
As a result of CCM implementation, they optimized their schedules and anticipated all possible activities. Product development was accelerated and risk management was improved. The machine was very quickly upgraded to identify COVID-19.
From the example, let’s return to the advantages of this method.
Benefits of the critical chain method
The critical path vs. critical chain can be compared based on their advantages.
The most vital benefit of CCM is that by entering scheduled activities, resources, durations, and logical relationships into a critical path Gantt chart or other diagram for this aim, it automatically creates the best possible schedule model with planned dates for completing all project activities.
Here’s a list of other facts that distinguish the critical chain method from its more simplified version.

- Focus on resource constraints. CCM primarily emphasizes resource constraints. It ensures that resources are available when needed and logically leads to shorter project durations.
- Advanced buffer management. CCM is known for incorporating project buffers to protect against uncertainties and delays. These buffers are strategically placed to safeguard the project’s completion.
- Reduced multitasking. CCM minimizes multitasking by allocating resources to tasks in a way that maximizes efficiency. This reduces the negative impact of task switching.
- Improved project reliability. Another evident benefit of CCM is that it’s designed to make project schedules more reliable by considering resource limitations and uncertainties, leading to better on-time performance.
- Enhanced collaboration. CCM also encourages better collaboration among team members and stakeholders by focusing on resource constraints and buffer management.
- Increased flexibility. The critical chain method looks flexible as it protects the project’s end date with buffers. This flexibility can be valuable in dynamic project environments.
Critical path vs. critical chain: what’s the difference?
Both of these types of scheduling methods can help ensure that project teams have their attention on the right parts of their projects.
A critical path is more focused on project duration and task dependencies, while a critical chain takes resource constraints and uncertainties into account, emphasizing the efficient use of resources and buffers to mitigate risks.
What other differences based on the methods’ benefits can be marked between them?
- Concept. A critical path centers around task management, whereas the primary focus in the critical chain method lies in resource and buffer management.
- Resource management. The critical path method assumes the availability of all resources simultaneously, which is somewhat of an approximation. On the other hand, the critical chain method considers limited resources and optimizes their utilization to create a more realistic timeline.
- Buffer usage. In the critical path method, buffers are allocated for individual tasks within a project, while in CCM, additional time is allocated for the entire project.
- Delays. In the critical path method, team members can immediately initiate non-essential activities, potentially leading to delays. In contrast, CCM may experience delays in such tasks due to its resource-centric approach.
- Multitasking. CPM permits multitasking, enabling the concurrent completion of two activities on a critical path. The critical chain approach doesn’t support multitasking.
- Monitoring. While the critical path method may encounter task duration extensions when additional time is needed, the critical chain method assumes real-time monitoring and incorporates buffers for every task to ensure on-time completion.
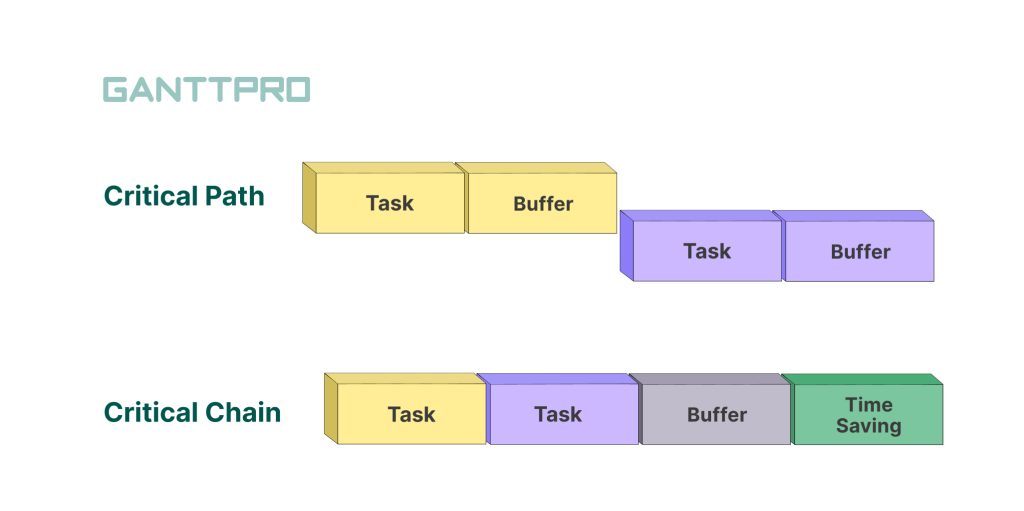
It was the basic information regarding the comparison of critical path vs. critical chain.
Now it’s time to learn a practical way to apply these methods and find a critical path using a professional project management tool.
How to use a critical path in GanttPRO
Professional project managers can use a variety of online solutions that help in identifying a critical path. Many of them allow for creating a visually appealing Gantt chart for this aim.
One of the most reliable and high-quality solutions based on a Gantt diagram is GanttPRO.
This efficient Gantt chart tool allows for establishing a detailed project schedule by creating tasks in the desired sequence. With its help, you’ll quickly understand that project planning, work management, progress tracking, and resource allocation in project management are easy practices.
GanttPRO comes with a simple and intuitive interface that doesn’t require much time to learn.

Professional project management software
Visualize a critical path on a handy Gantt chart.
Sign up for freeBesides the functionality for finding and managing a critical path, the Gantt chart maker offers many other useful features for advanced project management:
- Advanced planning.
- Task management.
- Portfolio management.
- Resource management.
- Time tracking.
- Budget management.
- Notifications.
- History of changes.
- Baselines.
- Export to PNG, PDF, XML, or Excel formats.
- Import from Excel, MS Project, and JIRA Cloud.
- Reporting.
- Useful templates.
Returning to the option of finding the most important tasks in your project, it is worth noting that you’ll need only a click to visualize these activities within your timeline in GanttPRO.
Such simplicity and power of the tool are appreciated by many professionals.
For example, Iqbal Jumabhoy, CEO of BlackBook Technologies (the app for tourists) assesses the role of GanttPRO and the power of a critical path in the projects of his company:
What I like about GanttPRO is that you can put everything in, you can sequence everything, you can assign multiple members to tasks, you can actually share messages and updates, and lastly, but this is very important: you can create a critical path. In our weekly meetings, we look through the critical path and we know exactly what is behind and who is behind it. This is very important when you are launching a new product.
How to apply a critical path in GanttPRO and where to find it in the tool settings?
We’ve prepared a quick tutorial with consistent steps. Let’s figure them out.
1. Project initiation
Everything starts with ideas. If you are confident in their viability and ready to turn all your initiatives into real tasks, then it’s time to place them on an online timeline.
It will not require much time. You can do it faster by collaborating with your team.
2. Task creation and distribution
To sort and organize your tasks into the right hierarchy, you’ll need a proven system.
GanttPRO provides a work breakdown structure that helps in distributing tasks according to their order and defining subtasks, presenting them in a logical sequence.
It’s important to consider start and end dates and the duration of tasks at this stage.
Distributing project activities among team members and assigning responsible people are also essential steps. In GanttPRO, you can do them in seconds.
3. Task dependencies and project milestones
The next stage on the way to identifying a critical path is connecting tasks with each other and defining the most weighty of them.
In GanttPRO, you can link all dependent tasks with the help of the drag-and-drop feature.
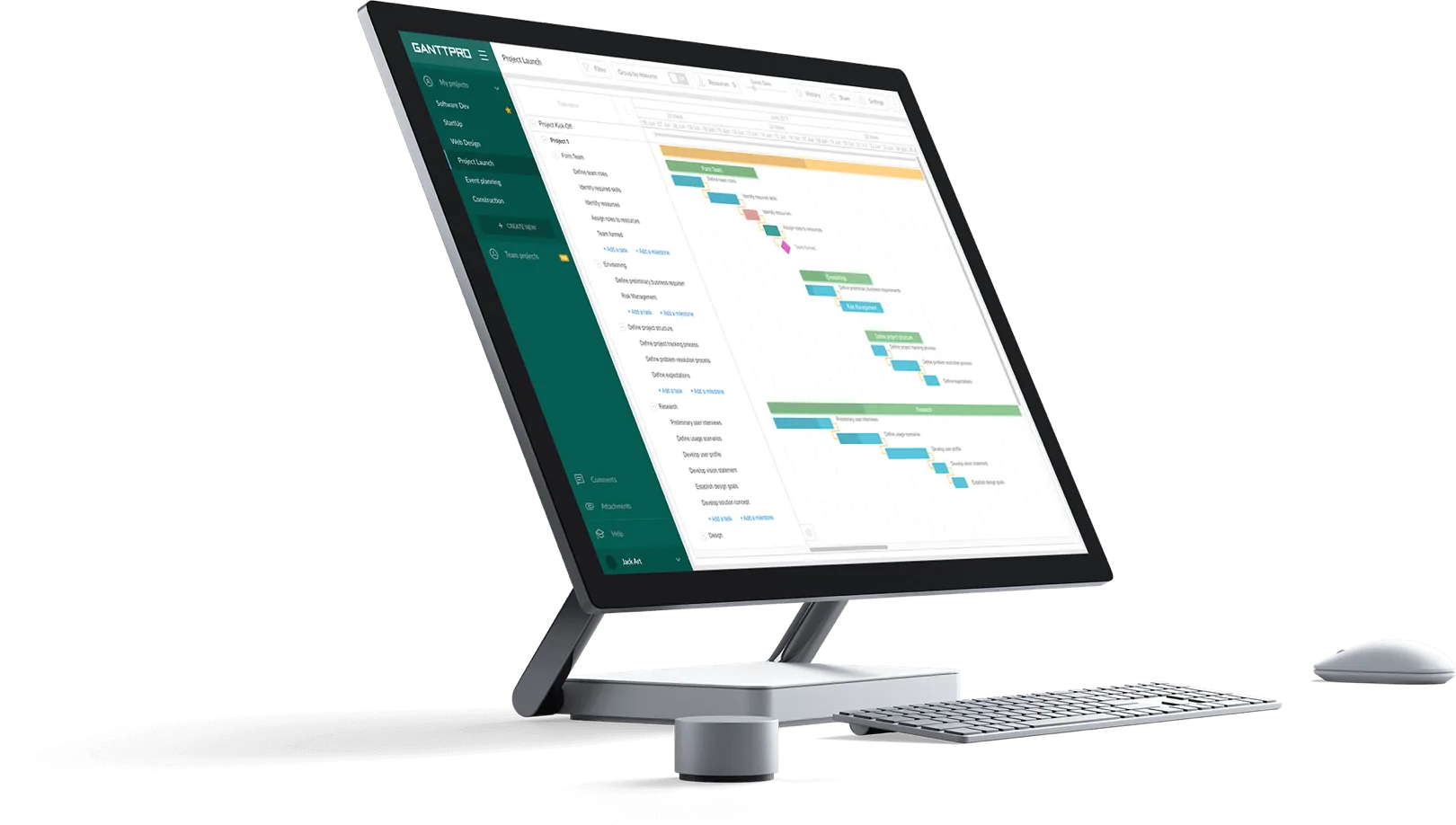
Marking key milestones is also an easy thing here because you’ll need only one click to visualize them. You can see it in the illustration below.
4. Critical path identification
When all your tasks, deadlines, dependencies, and milestones are clearly visualized on a Gantt chart, you can find a critical path for the entire project.
In GanttPRO, activating such a sequence of vital tasks takes just a few seconds.
To realize it, you should click on the button located in the top left corner of your screen.
The Gantt chart maker will reveal the path instantly, displaying the sequence of crucial tasks in your project in red.
This simplifies the representation of task order in your project without additional complexity.
The simple steps outlined above show the role and professional power of GanttPRO for identifying the most important tasks and their sequences in a project.
Please keep in mind that in case you have several critical paths, you’ll have a higher probability of schedule changes. Fortunately, GanttPRO is always ready to help and provide its functionality.
Project teams rely on GanttPRO and visualize the most essential tasks that impact project timelines, recognizing it as reliable critical path software.
Certainly, every single project has its own distinctiveness, encompassing various particular aspects and individual intricacies.
Nonetheless, drawing from the aforementioned steps, you will expedite the identification of this sequence within your own project with ease. No matter which method from the critical chain vs. critical path comparison you rely on.
Critical chain vs. critical path: explore and apply them for better project results
Critical path vs. critical chain is the pair of project management methods that both look at what important tasks need to be accomplished to complete a project and in what sequence these tasks need to be done.
However, these methods take different pathways to help PMs complete their work.
Both CPM and CCM have their unique advantages, and the choice between them depends on the specific needs and constraints of a project.
Choose the most appropriate method from the pair “critical path vs. critical chain” and take advantage of professional project management software like GanttPRO to find and manage critical paths efficiently.
Frequently asked questions about critical path vs. critical chain
-
The critical path and critical chain are both project management concepts. The key differences between them include: a critical path focuses on task management, while a critical chain centers around resource and buffer management; a critical path assumes simultaneous resource availability; a critical chain optimizes limited resources for a realistic timeline; a critical path allocates buffers for individual tasks, while a critical chain allocates a buffer for the entire project; a critical path allows immediate non-essential activities, potentially causing delays; a critical chain may experience resource-centric delays; a critical path permits multitasking; a critical chain doesn’t support it; a critical path may encounter task duration extensions, while a critical chain includes real-time monitoring and task-specific buffers for on-time completion.