What is Lean Project Management? Its Definition, Principles, and Methodology

Audio version:
It’s difficult to find a project where no problems occur. There will always be issues with tasks, deadlines, and assignees. No one and nothing will secure your plans from poor results.
To succeed and complete a project, every manager should have diversified knowledge in many spheres. And of course, it concerns methodologies. Among them are Work Breakdown Structure, Agile Project Management Methodology, Critical Chain Project Management, and some others. Also, it is a must for managers to set Project Management Smart Goals.
The list of project management methodologies won’t be full without one more approach. It’s Lean project management. Let’s figure out what Lean management means. Also, you’ll read about its origin and Lean approach to project management in general.

To start with, let’s learn what lean means. Its core concept is all about producing more value to customers and reducing waste. The Lean approach should result in an increase in quality with decreased costs.
Where Lean management came from
The Lean management term itself and the philosophy originated in Japan. In particular, there is an association of Lean management with Toyota Production System (TPS). The association is obvious as Toyota developed this Lean approach. Later it gave the birth to Lean manufacturing. As you see, it’s primary use was on a manufacturing floor. But today it has direct application in many other spheres. They include project management, software development, construction, etc.
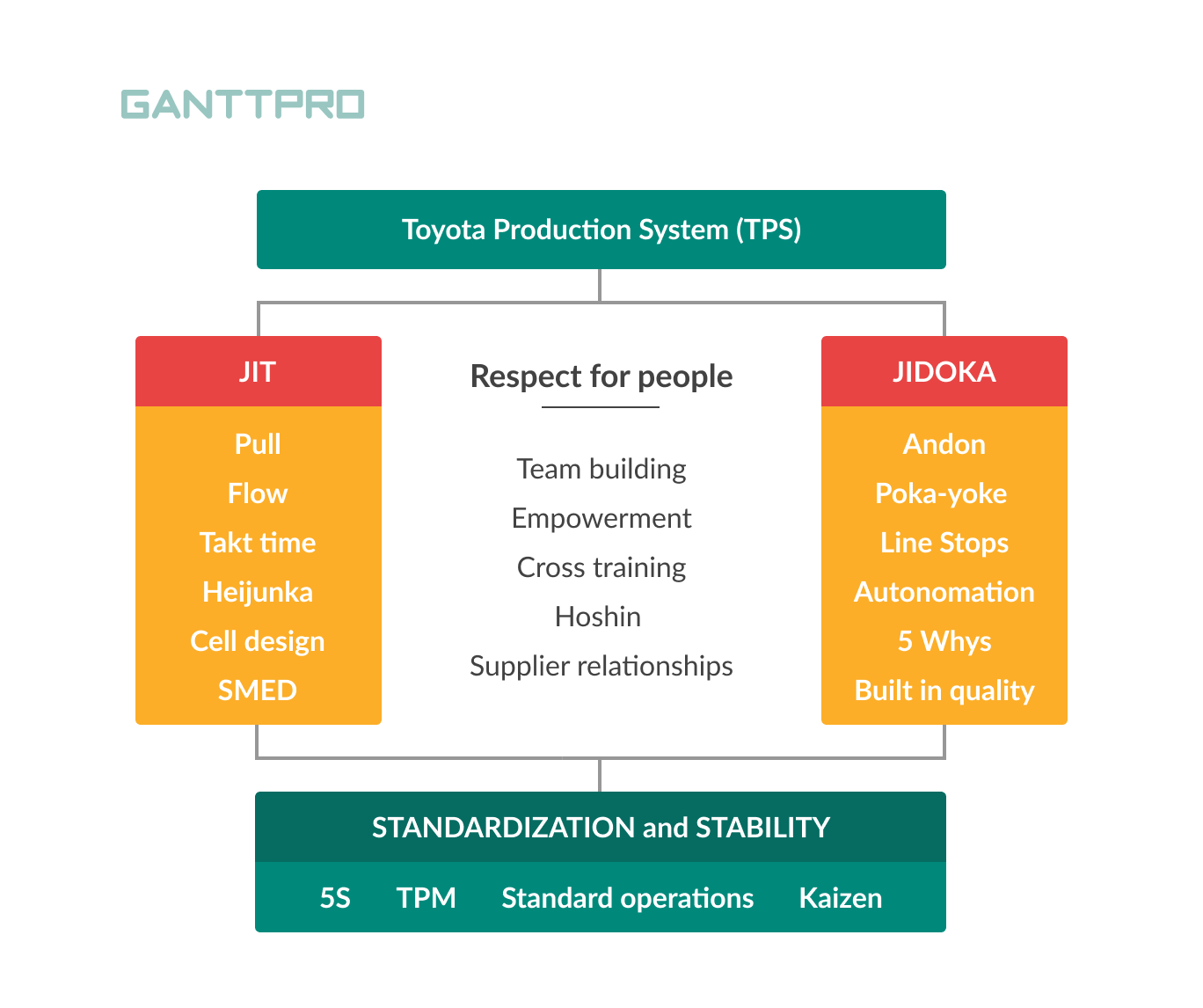
Toyota Production System (TPS)
To better understand core values of Lean management, let’s have a closer look at TPS.
Two basic concepts form Toyota Production System. The first one has a Japanese name Jidoka. The English translation is not 100% accurate but has a close meaning. It is «automation with a human touch». One of the basic Lean management principles has a reflection in it. To prevent waste, automation processes stop as soon as a problem occurs. So, Jidoka’s primary aim is to visualize a problem to enhance quality.
The second concept is «Just-in-time» (JIT). According to it, each process should produce only what is required for the next process. In short, it looks like «we make only what is in need now, when there is this need, and in the mount it requires». This approach should lead to productivity improvement.
Both approaches together make a continuous flow.
What is Lean project management?
Lean project management is a project management methodology that maximizes customer value and minimizes waste by optimizing the flow of materials or tasks through the system as a whole.
So, the emphasis in Lean project management is on improving processes and reducing waste. It considers all the processes in an organization with the goal to improve them. Also, Lean management helps to enhance efficiency and effectiveness of a project team.
On the contrary, Lean project management aims at eliminating waste of time and resources as one of the aspects of overall improvement. In the long run process improvement leads to a better value of a product or service.
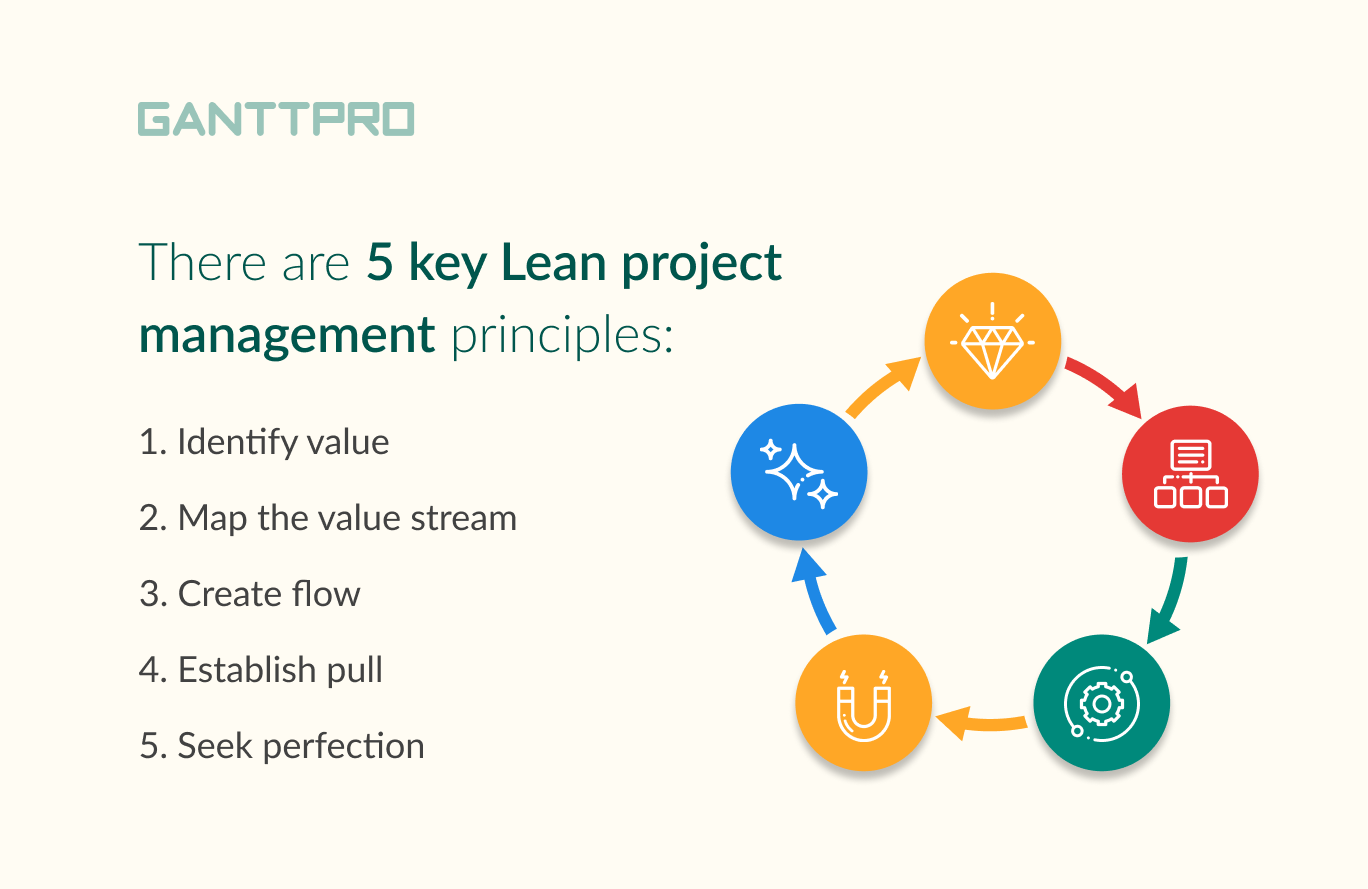
Lean management principles
- Value.
- Value streams.
- Flow.
- Pull.
- Perfection.
Value is the first and the core principle in the Lean management system. Before you start a project, define what will bring most value to customers. This understanding will help to work on the functionality that customers need. In other words, you need to define what your customer will pay for.
For example, in GanttPRO we constantly analyze all features requests. We count the number of them. Based on this number, we prioritize certain features. We make them our primary focus to improve our Gantt chart maker. Thus we move from release to release making our product better. This is how it looks with the first key Lean project management principle.
During the next step – value stream – managers create a map of the whole life cycle. It starts with needed materials and ends with a final delivery to a customer. To pursue the ultimate goals of Lean management – to reduce waste – it’s essential to value every step, process, feature, and materials. Thus you will identify whether each of them gives or does not give any value to the project. At this stage of Lean project management, you should eliminate everything without any value.
After you removed waste, there should be a smooth flow of your project. It should go without any interruptions and delays and move towards the final goal.
Pull requires a high level of flexibility. According to this Lean management principle, managers should take actions when a customer orders or dictates it. This is opposite to some traditional approaches of manufacturing project management. They include forecasts or schedules to push work. Thus, the Pull Lean management principle ensures that project teams won’t take any steps ahead of time.
After all, all four above-described steps should lead to perfection. But it is a step-by-step ongoing process. A pursuit of perfection is what makes you improve quality and eliminate waste and finally, make your Lean project management more efficient.
What is Lean methodology in project management?
Lean methodology in project management focuses on delivering a project with more value and less waste. It happens due to systematically eliminating waste in the value stream of the Lean manufacturing process.
There are three types in the Lean methodology. They are Lean Six Sigma project management (DMEDI), Deming Cycle (PDCA), and Kanban.
Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma (DMEDI) identifies primary reasons that caused problems in project management processes. It helps to reduce and eliminate wastage in time and resources.
As you’ve noticed, there is an acronym DMEDI in the name. These letters stand for Define, Measure, Explore, Develop, and Implement.
- Define scope and goals of your project. Also, this step includes identification of those features that your customer will value.
- Determine how you will quantify success and measure it throughout your project.
- Lean methodology is all about improvement. Explore how you can improve the ways of project accomplishment.
- After you define project scope and its deliverables, develop a solid plan.
- The final step is to launch and implement your project.
To analyze data and monitor an ongoing process of improvement, this method uses Lean project management tools and Lean project management software. Let me say a few words about them.
- Value stream mapping to document, analyze, and improve flows.
- Root Cause Analysis (RCA) to identify and eliminate issues that cause troubles.
- Customer feedback to understand what points of improvement are.
- Gantt chart to be aware of progress.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) to analyze performance.
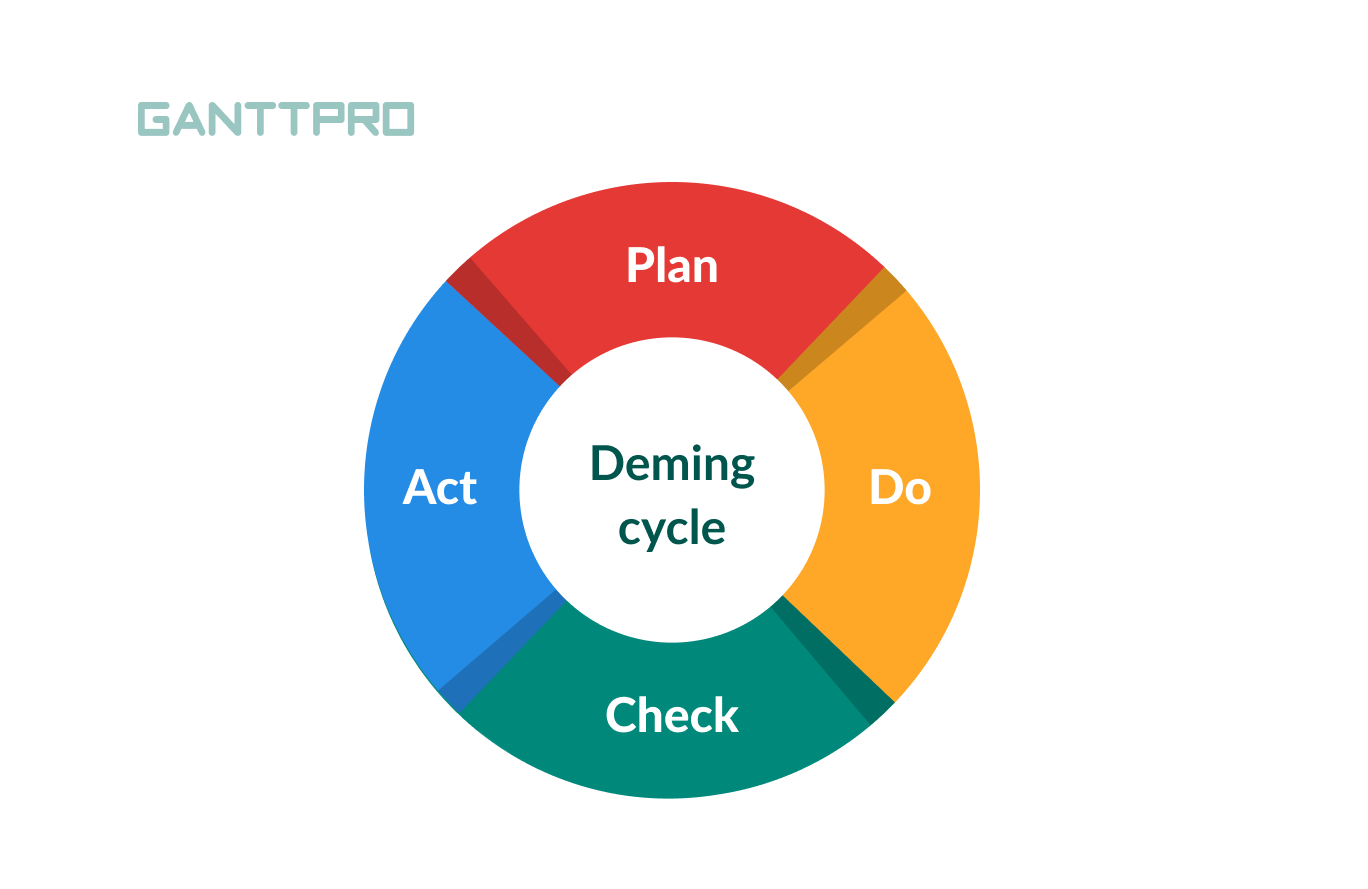
Deming cycle
PDCA, or Deming cycle, is a management method based on a philosophy of William Edwards Deming. He was a statistician, professor, lecturer, author, and management consultant. The method is used for controlling and, of course, continual improvement of project processes.
PDCA stands for Plan, Do, Check, Act. Sometimes the letter A stands for Adjust instead of Act.
- The Planning phase goes around assessing currents processes. During it, managers should also identify problematic points and figure out how to improve them.
- During the Do phase managers develop solutions.
- The third process – the Check phase – includes evaluations of all data gathered during the do phase. Based on it, managers make improvements.
- The Act phase includes implementation of solutions.
If you work on recurring projects, this Lean project management methodology will serve you well.
Kanban
The name of this method derives from the Japanese word meaning «card» or «visual signal». Again, as it is one of the Lean approaches, the main goal here is to improve project management processes. A manager and team members use a board with cards.
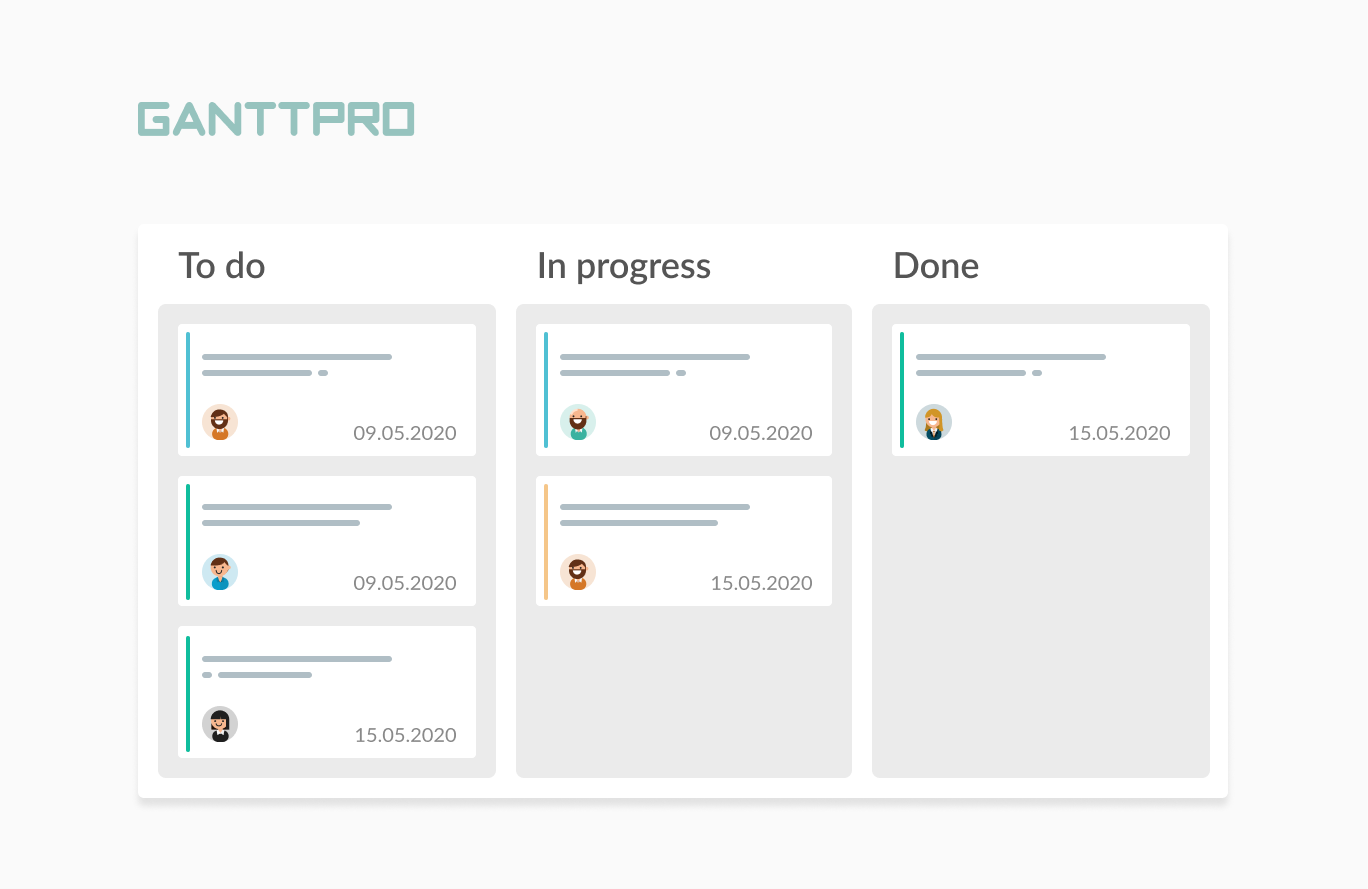
Work process here goes from the left to the right. Each column is a certain stage of tasks. Thus, it shows how the project is progressing. Usually, there are three columns: «Waiting» or «To do», «In progress» and «Completed work» or «Done».
But of course, there are some other Kanban board examples.
How GanttPRO lets managers work with a board
Even if you are great at methodologies and Lean project management methodologies in particular, without a special tool it is difficult to manage projects. To manage efficiently, managers should visualize everything in one easy-to-understand system. Here is where GanttPRO helps.
Yes, we know that GanttPRO is Gantt chart software. But we never stop improving our product. That’s why we implemented an absolutely new to our tool feature – a Board view. We pursued only one aim – to make your project management process smoother and more productive.
Now you can switch between a diagram view and a board view with tasks. You can find the switch at the top of the screen. Thus, you choose the way it is more convenient for you. In GanttPRO, you can set columns according to Status of tasks (open, in progress, done), Priority (highest, high, medium, low, lowest), and People.
Simply drag cards and drop them where you need to. All the changes you made in a diagram view will be reflected in a board view too. The same happens in the opposite direction.
So, why don’t you try GanttPRO?

Gantt chart project management tool
Plan and manage your projects with an online Gantt chart.
Sign up for freeHave you ever implemented Lean project management? Please, share your thoughts with us in comments!