Effective business outcomes depend on a healthy project lifecycle. Project managers should know what to do at each stage, including the critical path method identification.
This project management technique involves mapping out essential or critical tasks necessary to complete projects.
What is the value of determining the critical path in a Gantt chart, and why is the critical path method (CPM) necessary?
We’re here to help you figure it out. Let’s start with the critical path method definition.
Contents:
- What is the critical path method?
- Why is CPM important?
- Сritical path method example.
- Key steps in CPM planning.
- How to calculate the critical path method.
What is the critical path method in project management?
The critical path method (CPM) is a step-by-step management technique for project processes planning. It identifies critical and noncritical tasks and prevents timeframe problems.
Every project starts with a plan. It involves forecasting and setting a deadline for project completion. CPM helps managers be more precise as it allows them to identify which tasks cannot be delayed.
By the way, beginners should remember that CPM is a necessary part of project management certification.
The history of the critical path method
The concept of the CPM as a part of project management was developed in the late 1950s in the United States by James E. Kelley and Morgan R. Walker.
The method was used for agricultural projects and construction work. Kelley and Walker tried to find ways to reduce the costs associated with plant shutdowns and restarts caused by inefficient scheduling.
Instead of saturating the problem with additional labor, they understood that excess costs could be avoided. This is how the critical path method in construction appeared.
By the way, around the same time, a similar technique — PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique) was developed too.
Although the interest in the CPM had diminished by the early 1960s, some businesses began to apply it to oversee large projects (including Catalytic Construction and Mauchly Associates).
The usage of a critical path became much more widespread after the PC revolution. The detailed analysis of PM challenges resulting from the CPM approach prompted the development of the more sophisticated critical chain method (CCM). After that, the critical path vs. critical chain discussions became increasingly popular.
Nowadays, both approaches are adapted to different fields, including software development.
Why is the critical path important?
Why do project managers utilize the critical path method (CPM)? It provides valuable insight into project planning, task scheduling, and resource allocation.
Here are some detailed reasons why the method is worth your attention:
- Improves planning. You can use the concept to compare expectations with actual progress. The data used from your current projects can be applied to inform future plans.
- Helps to manage resources more efficiently. The method facilitates task prioritization, giving teams a better idea of how and where to deploy resources.
- Minimizes bottlenecks. You can lose valuable time due to unpredictable bottlenecks. Adding dependencies will give you a better understanding of which activities can be run in parallel or not. It will allow you to schedule accordingly.
The process of identifying the critical path in projects continues to get easier. When CPM was created, managers had to identify a critical path by hand. Now you can save time and avoid drawing tables and nodes using powerful critical path planners.
Advantages of the critical path method
The advantages and disadvantages of the critical path method are also a popular topic for discussion among project managers.
There are several benefits associated with the CPM.
Enhanced scheduling
The segregation of critical and noncritical tasks permits more effective scheduling of the tasks and the project as a whole. The scheduling process allowed through the critical path identifies those vital tasks to the efficient running of your project.
Understanding where the alterations can be made ensures that critical processes are not impeded, and your project remains on schedule.
Improved project management
We can’t evaluate the advantages of using the critical path method without mentioning the benefits for PM.
With the help of the CPM, you can break apart substantial undertakings into elemental parts. This division creates individual and discrete tasks that significantly enhance and simplify project management.
The critical path also ensures the proper allocation of resources (including human resources).
More efficient distribution of human resources
Often managers say that something went awry concerning how human resources were allocated.
There are several ways to distribute human resources defined through the critical path. Thanks to the CPM, newer team members can be placed on noncritical project elements. They have a chance to learn more about the entire project, accomplish meaningful milestones, and not cause an interruption on project flow.
Cost/budget control
Completing work within budgetary parameters is crucial. When the budget is tied to subtasks rather than the project as a whole, financial expenses issues are recognized easier. So you can address them more effectively and in a manner that can save overall budgetary parameters.
These were not all of the critical path method advantages, and you can easily add your own to this list.
What about the disadvantages of the critical path method?
Disadvantages of the critical path method
CPM provides not only advantages but can be associated with some pitfalls. Here are some of them.
Poor adaptation to change
It doesn’t adapt well to making changes on the fly. If you manage a stable and predictable project, then the method can be helpful, but if you have to improvise a lot, then it’s not very useful.
Inability to determine the exact duration of tasks
Perhaps, you’ll have to guesstimate many project task durations. It will make a project timeline less reliable and CPM less useful.
A lot of time and effort required
Generating a critical path method diagram can take a lot of time and effort.
Constant resource planning required
If you do not control the resources you need to complete the critical path on deadline; your schedule may be hopelessly optimistic.
Are you already tired of dry theory? Now is the time for one of the real-life critical path examples.
Critical path method example with solution
The more complex the project, the more difficult it will be to figure out how to find the critical path. Here we’re considering a simple example. (But if you want complicated ones, you can always explore PM sites or read the best Agile project management books).
Critical path project management works perfectly for projects with short deadlines. So let’s say the purpose of our project is to plant a garden in a backyard. Now we need to set all the ways and steps to show us how to grow the first tree.
To complete this project successfully, we need to list all the tasks that should be done:
- Choose a place in the backyard.
- Buy a shovel.
- Choose the right seeds.
- Dig a hole.
- Fill the hole with water.
- Plant a tree.
As you can see, some of the steps cannot start before the others are finished because they are dependent. The steps “Dig a hole”, “Fill the hole with water”, “Plant a tree” are sequential activities because they must be done in a specific order.
In our example, these three steps and the first one (“Choose a place in the backyard”) are the most essential critical actions to get the solution. And they should be placed on the critical path for our project.
The main idea is that we cannot start some activities or steps until the others are finished.
Now it’s not difficult to calculate the length of the project. We can determine the approximate start time for every step on the critical path.
- Choose a place in the backyard – 30 minutes.
- Buy a shovel – 30 minutes.
- Choose the seeds – 30 minutes.
- Dig a hole – 10 minutes.
- Fill the hole with water – 5 minutes.
- Plant the tree – 15 minutes.
If we summarize the durations of all the critical tasks, we will get the time that we need to complete our project. In our critical path example, we need 2 hours.
Working with CPM can include six consistent steps. Have a look at how CPM project management can be used in practice.
6 key steps in CPM planning
Let’s learn more about these consistnt steps.
1. Make your activities specific
Identify every task in your project. The list of specific activities should include only higher-level activities. It will divide the tasks into manageable sections. Your structure may look like lists, tables, or tree structures.
2. Set dependencies
Some activities will start when others are complete. If you list the predecessors of every action, it will help you to identify the correct order.
3. Visualize a critical path
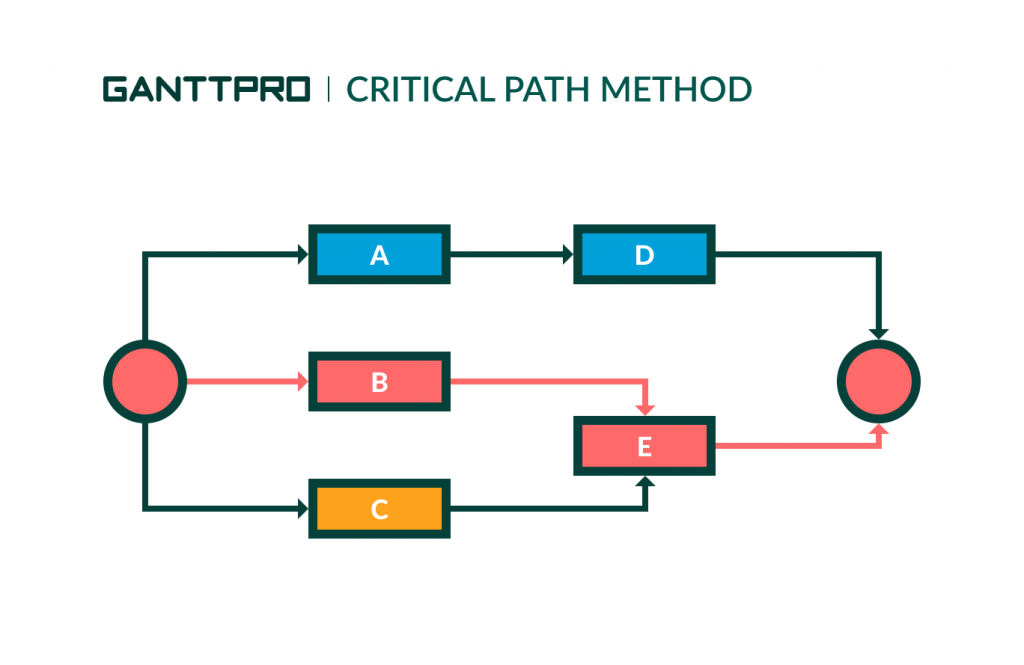
Now you have your identified activities and dependencies, so you can draw the critical path network diagram (the critical path chart).
Project managers use critical path network diagrams to view projects broken down into separate tasks. Boxes, arrows, and circles help to visualize the activities and dependencies. You should name each activity and highlight the paths.
There is no need to draw CPM diagrams on paper because you can use the helpful software for this purpose.
Online software for creating and managing Gantt charts
Manage multiple projects simultaneously and show critical paths on an online Gantt chart.
Sign up for free4. Estimate the time of activity completion
Even if you do not have enough experience, you may estimate the time required to complete all your activities. The measure can be a day or a week. It depends on how small or complex your projects are.
5. Find critical paths
To identify a critical path, you need to determine the main parameters of your activities.
- The earliest start time (ES) is when an activity can start once the previous dependent activities are completed.
- The earliest finish time (EF) is ES + the period required to complete the activity.
- The latest finish time (LF) is when an activity may be completed without any delays.
- The latest start time (LS) is the period required to complete the activity.
Pay attention to the float time between ES and LS or between EF and LF. During this period, your activity can be delayed without delaying the finish date of the project.
Using the network diagram, you can identify the longest path of any activity and the longest sequences. If you need to accelerate your project, you should reduce the time for critical path activities.
If you have several critical paths, you will have a higher probability of the schedule changing.
6. Update your diagram and watch the progress
The diagram should be updated to give you a chance to recalculate a critical path. Now you will have a more realistic view of your project.
How to calculate the critical path method in project management?
You can choose at least two ways to delegate it to software – rely on your Gantt chart software and enable this option in settings (like in GanttPRO) or use another critical path method calculator.
Suppose you rely on external tools to calculate the critical path. In that case, you need to fill in the following information:
- Successors.
- Predecessors.
- Duration.
- Early start time.
- Early finish time.
- Latest start time.
- Latest finish time.
- Slack time.
After that, your critical path will be calculated.
It doesn’t look very convenient, right?
However, some people still rely on such tools. For example, they utilize MS Excel striving to calculate a Gantt chart critical path.
Excel doesn’t have a feature that allows its identification. You’ll need to customize it a little bit to find the critical path on your own.
Frankly speaking, this is not a very simple (and for someone, a rather complicated) way. It requires creating the precedence diagram, preparing a spreadsheet, and building a Gantt chart for a visual representation of your projects.
However, project management professionals and business owners prefer more reliable and high-quality solutions.
We are pleased to remind you about the GanttPRO functionality, which will help you understand that identifying the critical path in your project is an easy task.
Teams choose GanttPRO to identify the most important tasks that impact project timelines, considering it trustworthy critical path software.
Gantt chart critical path calculation with GanttPRO
GanttPRO can do all the hard work for you. It will be easy to find the critical path in this Gantt chart maker with just a couple of clicks.
How do you enable a Gantt chart critical path in GanttPRO?
First, create your project and set all the tasks and subtasks. Set start and end dates, durations and identify all predecessors.
Then determine all required dependencies and project milestones. The drag & drop feature will help you to do it quickly.
Now you can adjust the view of your project to identify the critical path. Open Settings and click to switch on the critical path. This chain of important tasks will be shown in red.
Take the most out of the critical path method
The critical path method CPM is a multifaceted approach to project management, especially for more complicated tasks. At the heart of this method is the definition of critical vs. non-critical activities.
The ultimate aim is to undertake your project efficiently, with milestones being met without delays and interruptions.
If you apply the CPM critical path method, you’ll see that path identification is required for any planning phase. It’ll give you the correct completion date of projects and the flexibility to float activities.
To sum it up, we’d like to remind you once again that the critical path method scheduling is a powerful and effective way of assessing:
- Your tasks that must be carried out.
- All parallel activities.
- Task priorities.
- The sequence of scheduling and timing.
- The shortest time for your project to complete.
- All resources that you need to achieve the goal, etc.
With the critical path method in project management, you can focus your efforts on professional work optimization.
What do you think about it? Have you applied the CPM? Feel free to share your experience.